Bitrace | Web3 Anti-Fraud Handbook

In the digital era, cryptocurrency and blockchain technology have become increasingly important in the global financial system with their unique appeal and potential. However, this field, full of innovation and opportunities, also harbors various frauds and security threats. To help users better identify and avoid these potential risks, the Bitrace team has carefully compiled the Web3 Anti-Fraud Handbook, which provides in-depth analysis and detailed breakdowns of the fraud techniques that crypto users may encounter at different stages of their journey, using real-life cases. The goal is to equip investors with practical anti-fraud skills.
As a professional regtech company, Bitrace not only focuses on theoretical research and risk data monitoring but also pays close attention to real-time asset security incidents. Over the past year, we have received nearly a thousand cases through various channels, assisting victims in tracking and recovering funds. Through in-depth exchanges with numerous victims, Bitrace has accumulated valuable first-hand experience, gaining a deeper understanding of victim psychology, common techniques used by criminals, and prevalent scams in the cryptocurrency space. This solid foundation of practical experience and case support has contributed to the creation of the Web3 Anti-Fraud Handbook.
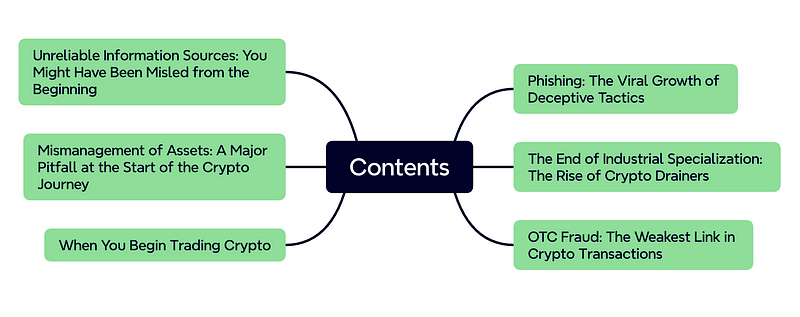
The Web3 Anti-Fraud Handbook is available in both Chinese and English and will delve into six major topics, gradually progressing from identifying unreliable information sources to addressing common pitfalls in asset management, investment traps during transactions, phishing attacks, and crypto drainers at the end of the fraud chain, as well as OTC scams that may occur when cashing out.
Unreliable Information Sources: You May Be Deceived from the Start
Many investors first encounter crypto-related concepts through social media platforms, online communities, or other channels where information can be mixed with misleading content. Even experienced investors must sift through a lot of noise and rumors to find genuinely useful information, and inexperienced investors are more likely to be swayed by fraudulent messages. As a result, many fraudsters exploit the existing information gap to deceive outsiders who lack relevant knowledge, using tactics such as distorting or fabricating facts, stealing account keys, and tricking users into granting access to their accounts.
Seemingly harmless but dangerous QR codes in short videos, social media, and romance scams often exploit people’s curiosity, trust, and emotional needs, luring investors into traps. The Web3 Anti-Fraud Handbook will teach you how to identify these scams and avoid being deceived from the very beginning.
Improper Asset Management: The Hidden Pitfalls at the Start of Your Crypto Journey
Unlike traditional Web2 platforms with centralized account login and verification systems, blockchain wallets and other Web3 infrastructure do not store user identity information or account access. There are also no mechanisms for account recovery, re-linking, or identity verification, which are common in Web2 software. This means that Web3 users must manage their own keys. Losing these keys will result in permanent loss of control over on-chain identity, while leaking them may lead to theft of on-chain assets.

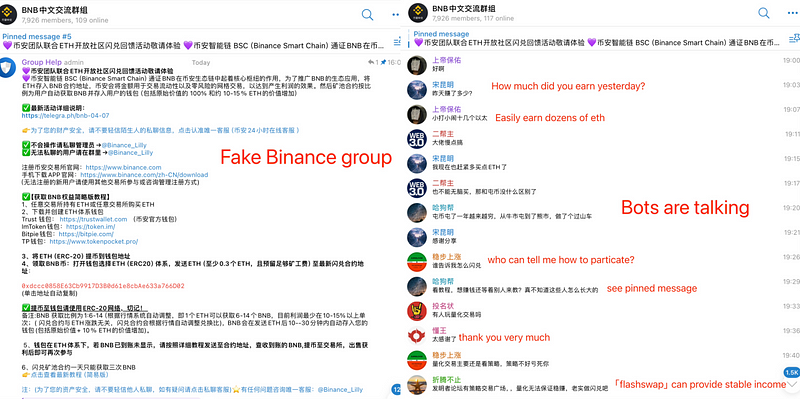
Some scammers take advantage of investors’ lack of knowledge about blockchain wallets by using various methods to obtain seed phrases, private keys, or wallet access permissions to steal assets. The Web3 Anti-Fraud Handbook will expose common scams like fake wallet apps, multisig payment fraud, authorization scams, fake Telegram scams, and hardware wallet Handbook fraud.
When You Start Trading Crypto
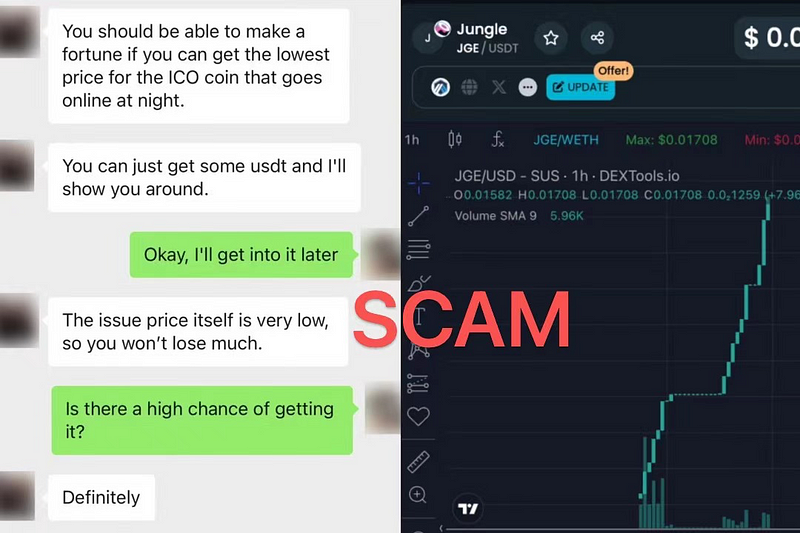
Do you believe there are sustainable financial products in the crypto market offering annual returns over 50%? Do you think you can make steady profits by staking stablecoins in a “mining pool”? Do you assume that participating in staking activities from the “official exchange” by purchasing a certain token will guarantee easy profits? If your answer is “yes” to all these, you might be in danger.
We will explain high-yield trading scams, Ponzi token fraud, fake Binance mining pool scams, fake OKX public chain scams (claiming USDT to receive OKT), liquidity exit scams, and other real cases to reveal the truth behind them.
The Viral Growth of Phishing
Phishing is an attack technique where deceptive emails, messages, calls, or websites are used to lure users into disclosing sensitive information or performing malicious actions. In the traditional internet era, phishing was usually aimed at obtaining victims’ cash or virtual assets. However, with the rise of the crypto economy, more fraudsters are targeting crypto assets.

Three common phishing methods targeting crypto assets are address poisoning, advertising tokens, and clearance messages. The Web3 Anti-Fraud Handbook will cover these in detail.
Crypto Drainer: The End of the Fraud Chain
A drainer is malicious software designed to drain cryptocurrency wallets. It is rented out by its developers, allowing anyone to pay and use it to commit theft.
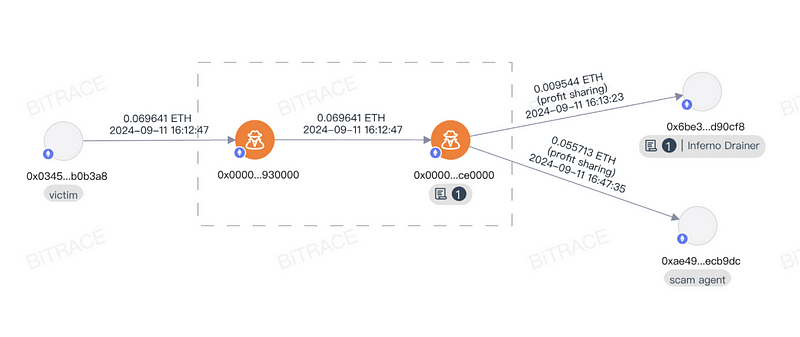
Crypto drainers reverse-engineer popular cryptocurrency wallet software, modify specific code to obtain the target’s seed phrase, and even develop management systems for large-scale key management, enabling operators to transfer funds with a single click. Techniques like address poisoning, fake official social accounts, and arbitrage scams, which trick victims into handing over token permissions, often have professional Crypto Drainers providing technical or operational support behind them.
OTC Fraud: The Weakest Link
In some countries or regions, over-the-counter (OTC) trading is the most common way for crypto investors to convert fiat currency into crypto. These OTC activities can take place on centralized platforms, online groups, or in person. However, regardless of the setting, OTC activities are always at risk of fraud, including fiat theft, crypto theft, and even personal safety threats.

The Web3 Anti-Fraud Handbook lists common fraud tactics such as exchange broker scams, offline trading fraud, and offline multisig scams.
Final Thoughts
Compared to other fields, the Web3 industry has higher entry barriers, which include technical knowledge, usability of infrastructure, and access to accurate information. Newcomers who are blindly confident and ignore these barriers often fall into traps. At the end of the Web3 Anti-Fraud Handbook, we provide some security advice and guidance on what to do if you fall victim to fraud.
Before you embark on this learning journey, we want to emphasize that anti-fraud is a continuous process. Fraud techniques are constantly evolving, so staying vigilant and continually learning is the key to protecting yourself. We encourage you to treat this Handbook as a starting point to keep exploring and updating your knowledge. Bitrace will also continue to share and analyze the latest security incidents, uncovering the fraud techniques involved.
To download the full version of the “Web3 Anti-Fraud Handbook,” please visit https://bitrace.io/en/blog.
Contact us:
Website: www.bitrace.io
Email: bd@bitrace.io
Twitter: @Bitrace_team
LinkedIn:@bitrace tech