Hidden Traps in the App Store: Exposing Fake Cryptocurrency Apps

The cryptocurrency boom has ushered a multitude of related apps into mobile app stores, providing users with tools for trading, investing, and managing digital assets. However, amidst these legitimate offerings, there are also meticulously disguised fraudulent apps that pose a threat to users’ asset security.
This article will use Apple’s App Store as an example to reveal the existence of fake cryptocurrency apps, analyze the reasons behind this phenomenon, and illustrate the dangers posed by high-quality counterfeit apps through real cases, aiming to raise user awareness.
The Current State of Fake Cryptocurrency Apps
Magic Eden and Jupiter, being highly renowned in the cryptocurrency space, have become targets for scammers to create counterfeit apps.
Magic Eden is a popular multi-chain NFT marketplace that offers users a platform to buy, sell, and discover digital artworks. However, on March 7, a team member of Magic Eden, Voh, discovered that there were fake apps on the App Store exploiting Magic Eden’s reputation to conduct scams. These fraudulent apps mimic the official website and user interface to deceive users into downloading and using the app. They then prompt users to provide sensitive information such as wallet private keys, leading to scams.
Voh mentioned, “The app is region-specific, and users in the United States cannot access it. Since there is no official Magic Eden mobile app on the iOS App Store and Google PlayStore, unsuspecting users find it challenging to discern the authenticity of this malicious application.”

Similarly, the decentralized exchange Jupiter based on Solana has also seen counterfeit apps. The comments section is filled with “SCAM ALERT” warnings. Victims downloaded the app from the Apple App Store, linked their wallets, and authorized transactions, resulting in the theft of $1250. Additionally, the app steals users’ seed phrases for further theft.
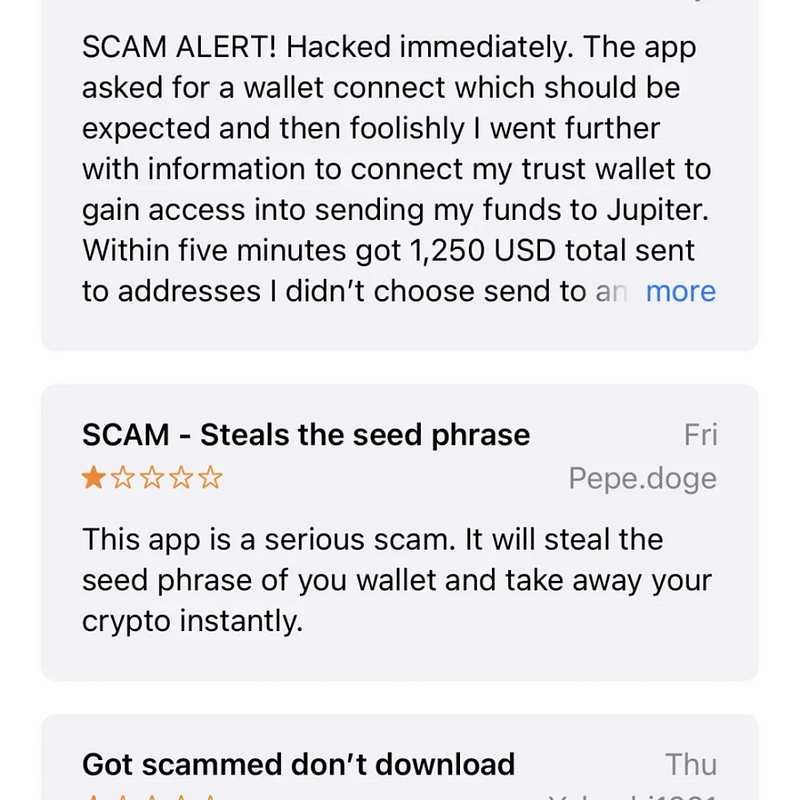
Jupiter Scam Address Analysis
Victim KryptoSub reported on social media that after downloading a fake Jupiter app from the App Store and linking their wallet, their seed phrase was stolen, resulting in the loss of all their on-chain assets. We conducted a further analysis based on the scam address 0x9e82530383d81725ec950ee51d116bde8bdc859e provided by KryptoSub.
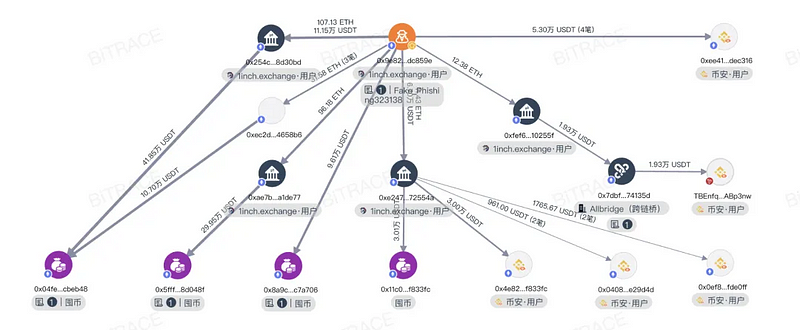
We found that from 2024–01–11 20:21:23 to 2024–03–30 09:19:59, the address stole the seed phrases of 298 suspected victims and laundered the funds, with a transaction volume of 353.6 ETH and 330,500 USDT. The incoming cryptocurrencies to this address were mostly various altcoins, which the hacker exchanged for USDT via 1inch. The funds were then stored in four different addresses, with some profits transferred through the Allbridge cross-chain bridge or directly to the Binance exchange. The address has now been flagged as a phishing address by Ethereum scam and ceased its phishing activities as of March 30.
It is evident that the threat of fake cryptocurrency apps is real and urgent. These fraudulent activities not only harm users but also negatively impact the reputation of the related brands. The cryptocurrency boom demands a higher level of scrutiny for app listings in mobile stores like the App Store.
Why Fake Apps are Rampant
Vulnerabilities in the Review Process: Despite Apple’s stringent app review process, some fraudulent apps still manage to slip through. Developers may exploit loopholes in the review process, allowing counterfeit or malicious apps to temporarily pass. Apple typically relies on automated tools and manual checks to assess app safety. Once an app is approved and listed, if it is later used for malicious purposes, it takes some time for Apple to detect and remove it. Criminals exploit this time lag to quickly spread malicious software, causing harm to unsuspecting users.
Misuse of Technical Methods: Malicious developers may also use advanced technical methods to evade security checks. Techniques like code obfuscation and dynamic content loading can conceal the app’s true intentions, making it difficult for automated security tools to identify its fraudulent nature. These methods provide a layer of protection for fake apps, making them appear legitimate during the review process.
Exploitation of User Trust: Fake app developers often mimic the appearance and names of well-known apps, exploiting users’ brand recognition and trust. Users generally believe that apps on the App Store have undergone rigorous screening, so they may not conduct necessary checks, making them more susceptible to scams.
In Conclusion
To prevent such situations, app stores like the App Store should continuously improve their app review processes. Official projects should promptly debunk fake apps. Cryptocurrency users should take preventive measures, such as checking developer information, carefully examining app ratings and feedback before downloading, and promptly reporting suspicious apps.
Contact us:
Website: https://www.bitrace.io/
Email: bd@bitrace.io
Twitter: https://x.com/Bitrace_team